This is an old revision of the document!
THEMIS Solar Telescope
|
The “Télescope Héliographique pour l’Étude du Magnétisme et des Instabilités Solaires” (THEMIS) of CNRS-INSU is a 1-meter-class optical solar telescope, primarily dedicated to studying solar magnetism and the dynamical processes within the Sun’s atmosphere (such as sunspots and solar flares). THEMIS can also perform observation of near-Sun objects such as Mercury and comets. THEMIS is located at the Teide Observatory of IAC, with a base office in La Laguna, in Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain. ¡¡¡ Call for the 2026 observing campaign is open !!!
November : First screw of the Italian IBIS 2.0 Spectro-imager @ THEMIS. Click for information on: How to reach THEMIS locations ; How to contact the THEMIS team |
Overview of telescope status
|
|
The THEMIS telescope and its science
Technical & scientific information about THEMIS
THEMIS scientific objectives
THEMIS administrative structures
Observing with THEMIS
Information for research scientists wishing to observe with THEMIS
2026 observing campaign
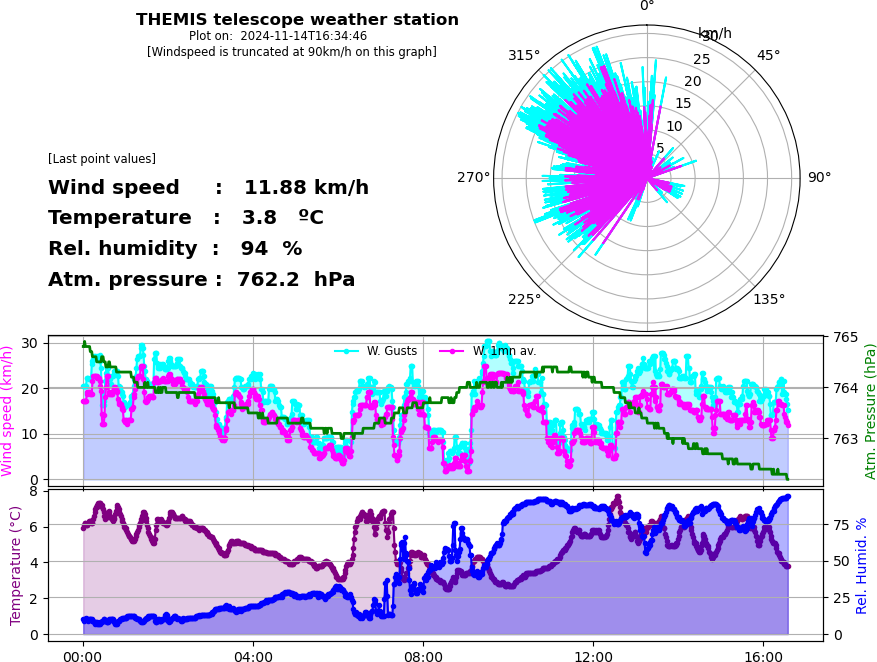
Weather at THEMIS location and weather forecast
THEMIS data products & data access
THEMIS Scientific research & results
Scientific research with THEMIS
THEMIS scientific highlights and news
THEMIS observations and media galleries
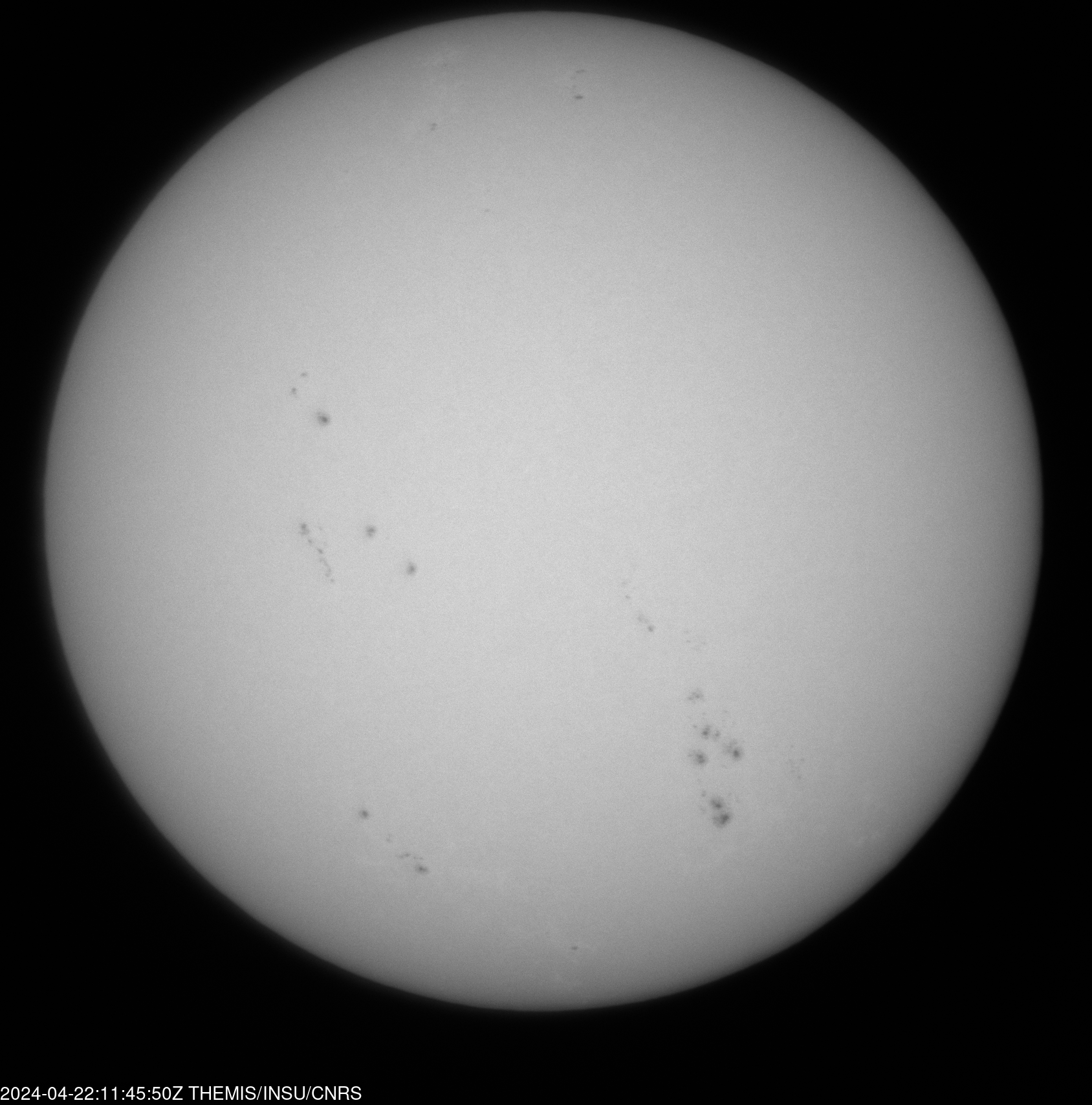
THEMIS image of the month: November 2025
|
Measuring magnetic field signature in the solar atmosphere is the “raison d'être” of THEMIS. Since its renovation, the THEMIS team has had as a main objective of producing vector magnetograms (maps of the magnetic field vector) while observing with the THEMIS adaptive optics (TAO). This December 2025 image of the month, presents one of the ultimate steps toward this goal, presenting the so-called Stokes maps that describe the polarisation of the light. The figure shows that in the centre of the Fe I line (at 630,1 nm) a strong polarization signal is captured by the spectropolarimetric measurement of THEMIS in active region NOAA 14100, obtained in May, indicating of the presence of magnetic field. In the continuum near that line, no polarisation signal is observed, confirming the absence of polarisation contamination in THEMIS light path. From such Stokes map, a magnetic inversion code shall then be used to determine the magnetic fields that could induce these light polarization signal, and thus produce magnetograms with TAO. |